- Tableau Tutorial
Tableau Public is a free platform to publicly share and explore data visualizations online. Anyone can create visualizations using either Tableau Desktop Professional Edition or the free Public Edition. With millions of inspiring data visualizations, or “vizzes” as we affectionately call them, anyone can see and understand vizzes about any. Tableau is a Business Intelligence tool for visually analyzing the data. Users can create and distribute an interactive and shareable dashboard, which depict the trends, variations, and density of the data in the form of graphs and charts. Tableau can connect to files, relational and Big Data sources to acquire and process data.
- Tableau Data Sources
- Tableau Worksheets
- Tableau Calculations
- Tableau Sort & Filters
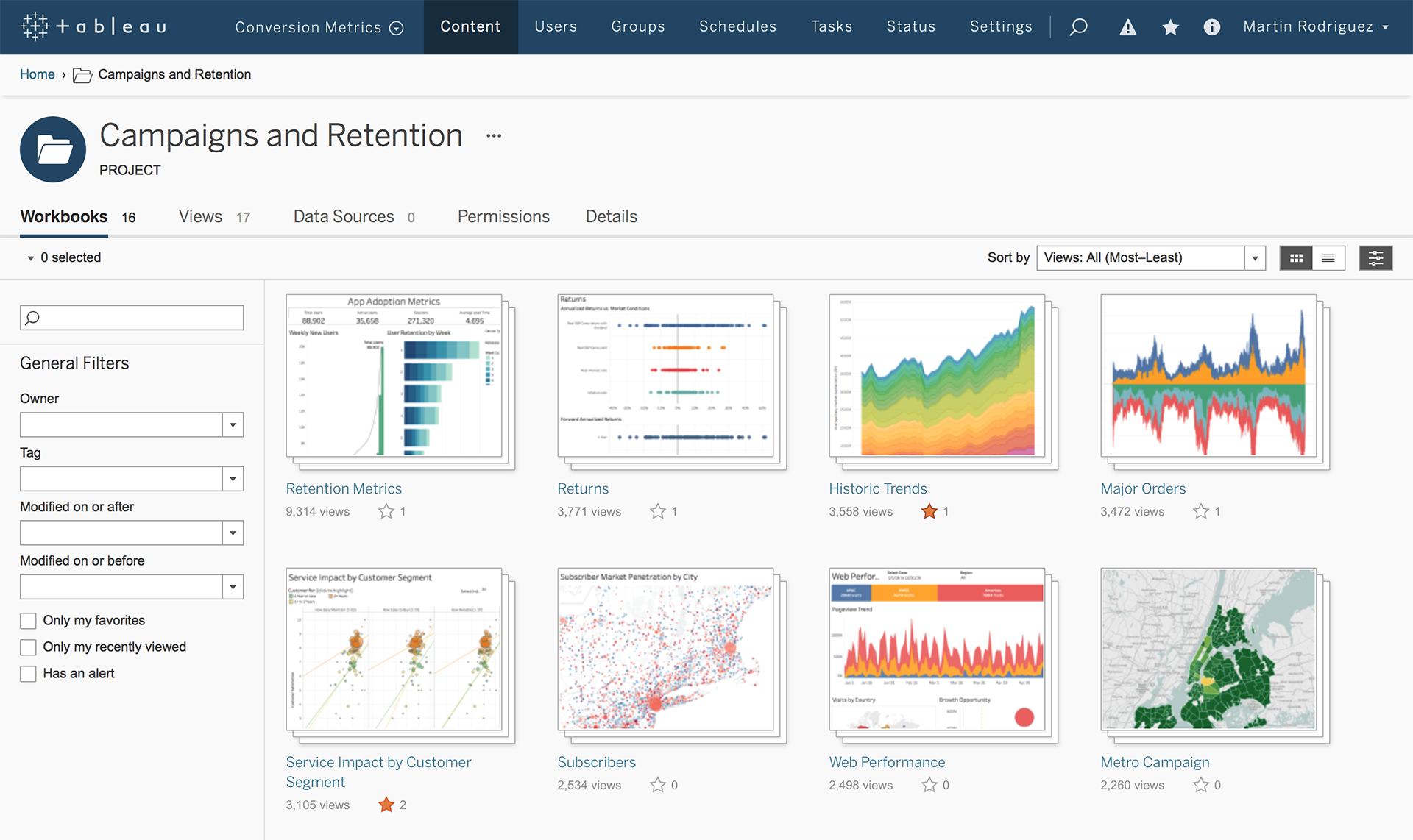
- Tableau Charts
- Tableau Advanced
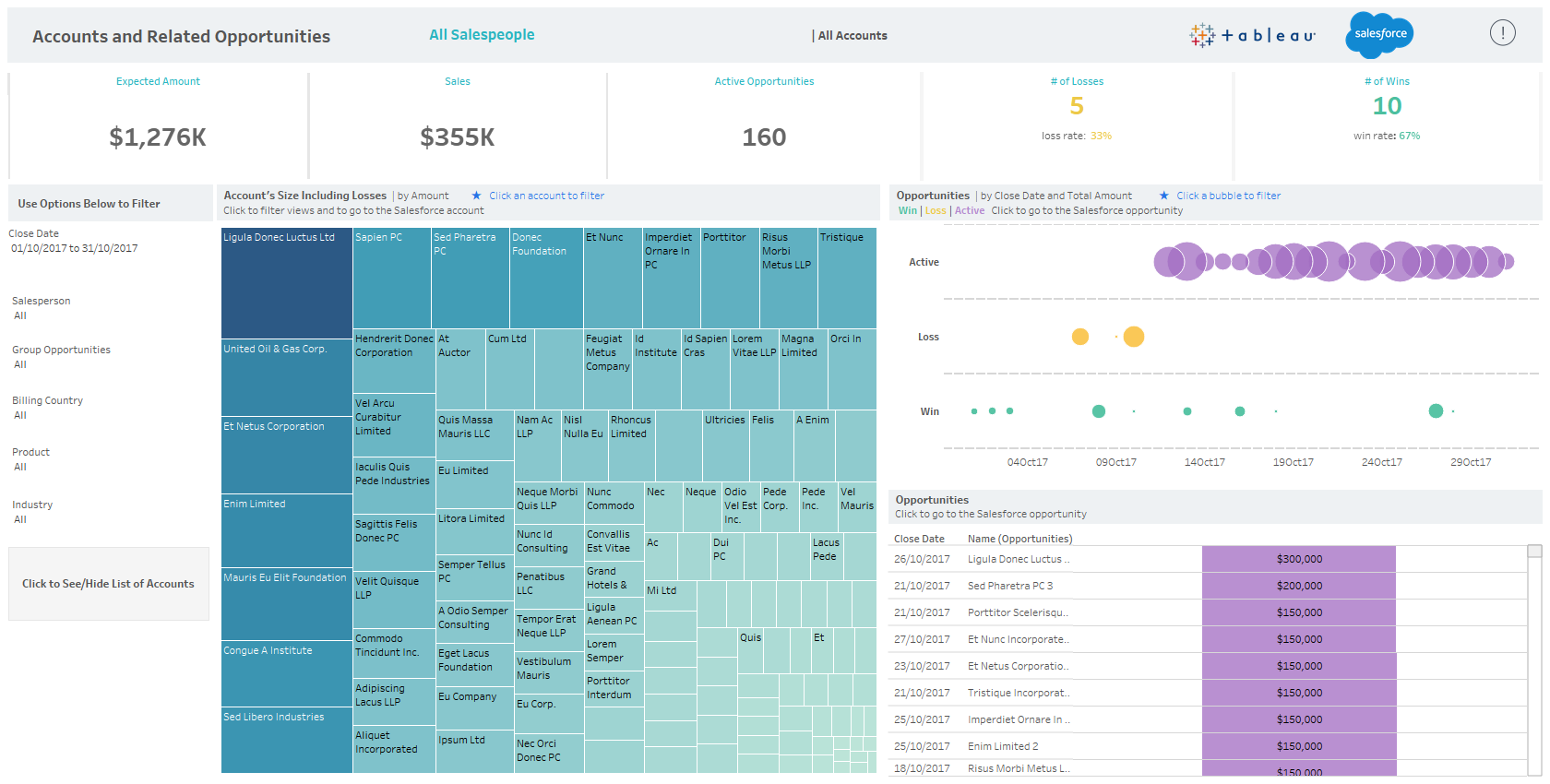
- Tableau Useful Resources
- Selected Reading
An operator is a symbol that tells the compiler to perform specific mathematical or logical manipulations. Tableau has a number of operators used to create calculated fields and formulas.
Following are the details of the operators that are available and the order (precedence) of operations.
Types of Operator
- General Operators
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
General Operators
Following table shows the general operators supported by Tableau. These operators act on numeric, character, and date data types.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| +(addition) | Adds two numbers. Concatenates two strings. Adds days to dates. | 7 + 3 Profit + Sales 'abc' + 'def' = 'abcdef' Adobe illustrator cs3 crack for mac. #April 15, 2004# + 15 = #April 30, 2004# |
| –(subtraction) | Subtracts two numbers. Subtracts days from dates. | -(7+3) = -10 #April 16, 2004# - 15 = #April 1, 2004# |
Arithmetic Operators
Following table shows the arithmetic operators supported by Tableau. These operators act only on numeric data types.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| *(Multiplication) | Numeric multiplication | 23*2 = 46 |
| /(Division) | Numeric division | 45/2 = 22.5 |
| %(modulo) | Reminder of numeric division | 13 % 2 = 1 |
| ^(power) | Raised to the power | 2^3 = 8 |
Comparison Operators
Tableau Free Download
Following table lists the comparison operators supported by Tableau. These operators are used in expressions. Each operator compares two numbers, dates, or strings and returns a Boolean (TRUE or FALSE). Booleans themselves, however, cannot be compared using these operators.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = = or = (Equal to) | Compares two numbers or two strings or two dates to be equal. Returns the Boolean value TRUE if they are, else returns false. | ‘Hello’ = ‘Hello’ 5 = 15/ 3 |
| != or <> (Not equal to) | Compares two numbers or two strings or two dates to be unequal. Returns the Boolean value TRUE if they are, else returns false. | ‘Good’ <> ‘Bad’ 18 != 37 / 2 |
| > (Greater than) | Compares two numbers or two strings or two dates where the first argument is greater than second. Returns the boolean value TRUE if it is the case, else returns false. | [Profit] > 20000 [Category] > ‘Q’ [Ship date] > #April 1, 2004# |
| < (Less than) | Compares two numbers or two strings or two dates where the first argument is smaller than second. Returns the boolean value TRUE if it is the case, else returns false. | [Profit] < 20000 [Category] < ‘Q’ [Ship date] < #April 1, 2004# |
Logical Operators
Tableau New Orleans
Following table shows the logical operators supported by Tableau. These operators are used in expressions whose result is a Boolean giving the output as TRUE or FALSE.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| AND | If the expressions or Boolean values present on both sides of AND operator is evaluated to be TRUE, then the result is TRUE. Else the result is FALSE. | [Ship Date] > #April 1, 2012# AND [Profit] > 10000 |
| OR | If any one or both of the expressions or Boolean values present on both sides of AND operator is evaluated to be TRUE, then the result is TRUE. Else the result is FALSE. | [Ship Date] > #April 1, 2012# OR [Profit] > 10000 |
| NOT | This operator negates the Boolean value of the expression present after it. | NOT [Ship Date] > #April 1, 2012# |
Operator Precedence
The following table describes the order in which operators are evaluated. The top row has the highest precedence. Operators on the same row have the same precedence. If two operators have the same precedence, they are evaluated from left to right in the formula. Also parentheses can be used. The inner parentheses are evaluated before the outer parentheses.
Tableau Public
| Precedence | Operator |
|---|---|
| 1 | –(negate) |
| 2 | ^(power) |
| 3 | *, /, % |
| 4 | +, – |
| 5 | , >, <, >=, <=, != |
| 6 | NOT |
| 7 | AND |
| 8 | OR |